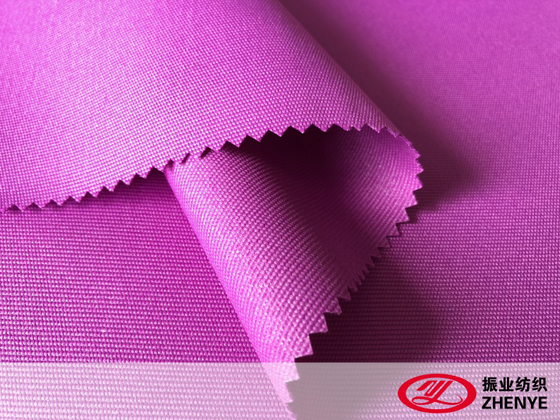
PVC fabric is widely used across many industries due to its strength, flexibility, and resistance to water and weather conditions. However, when choosing fabric, it’s important to understand that not all fabrics are created the same. Two common types are coated fabric and laminated fabric.
Coated PVC fabric is produced by applying a PVC layer directly onto a base textile, which is usually polyester or cotton. This process involves spreading or dipping the fabric into liquid PVC and then curing it to bond the PVC firmly to the textile surface. The coating can be on one side or both sides, depending on the intended use.
The PVC coating provides water resistance, durability, and protection against dirt and stains. Because the PVC layer is directly bonded to the textile, coated PVC fabric tends to be relatively flexible and lightweight. This flexibility makes it suitable for products like tents, tarps, banners, and protective covers that require some movement without cracking or peeling.
Coated fabric is generally easier to handle and can be sewn or welded, which adds to its versatility. Its surface texture varies depending on the coating method and additives used, offering options from smooth and glossy to matte finishes. This type of fabric is a popular choice for outdoor applications where waterproofing and moderate strength are important.
Laminated PVC fabric is made by bonding a PVC film onto a textile base. Unlike coated fabric, where the PVC is liquid when applied, laminated fabric involves attaching a pre-made PVC sheet onto the textile. The lamination process usually involves heat and pressure to ensure a strong, durable bond between the PVC film and the fabric.
Laminated PVC fabric tends to be thicker and heavier than coated.
fabric. The PVC film layer can be engineered to provide additional features such as enhanced abrasion resistance, better chemical resistance, and improved barrier properties. Because of these qualities, laminated fabric is often chosen for more demanding applications like inflatable boats, air-supported structures, and industrial curtains.
The lamination process gives the fabric a smooth, uniform surface that often has a higher gloss compared to coated fabric. This finish can improve aesthetic appeal and make the fabric easier to clean. However, laminated fabric is typically less flexible than coated fabric and can be more rigid, which should be considered based on how the fabric will be used.
Manufacturing Process: Coated PVC fabric applies liquid PVC directly to the textile, while laminated fabric bonds a PVC film to the textile base.
Weight and Thickness: Laminated PVC fabric is usually heavier and thicker due to the PVC film, whereas coated fabric tends to be lighter and thinner.
Flexibility: Coated fabric offers more flexibility, making it suitable for applications requiring movement. Laminated fabric is generally stiffer and better suited for static or heavy-duty uses.
Surface Texture: Laminated PVC fabric typically has a smoother, glossier surface. Coated fabric can have varied textures, from matte to semi-gloss.
Durability: Laminated fabric often provides better abrasion and chemical resistance, making it preferable for industrial or marine environments. Coated fabric offers good durability but may wear faster in harsh conditions.
Applications: Coated PVC fabric is commonly used for tents, tarps, banners, and protective covers. Laminated fabric finds use in inflatable products, heavy-duty tarpaulins, and industrial curtains.
When deciding which type of fabric is right for your project, consider the environment and requirements of your application. If you need a fabric that is lightweight, flexible, and easy to sew, coated fabric is often a better choice. For example, outdoor event tents or advertising banners benefit from the flexibility and ease of handling that coated fabric offers.
Both coated and laminated PVC fabric have unique advantages and limitations. Understanding the differences in their manufacturing, properties, and typical applications helps ensure you choose the right material for your needs. Whether flexibility and lightness are your priorities or durability and abrasion resistance are essential, PVC fabric offers versatile solutions that meet a variety of demands across industries.


 EN
EN
 English
English Español
Español 中文
中文
.jpg)
.jpg)
-1.jpg)
-1.jpg)