Clothing fabric, coating fabric, and polyurethane fabric are integral to modern textile manufacturing. Clothing fabrics form the core of apparel production, providing comfort, flexibility, and aesthetic appeal. Coating fabrics, including polyurethane fabrics, enhance base textiles with properties such as water resistance, durability, and abrasion resistance. These materials are widely used in garments, bags, furniture, and industrial applications.
Understanding the characteristics, production methods, and functional applications of these fabrics is essential to deliver high-quality, market-ready products that balance performance, comfort, and visual appeal.
.jpg)
1. Types of Clothing Fabric and Their Manufacturing Considerations
Key Points:
- Natural fibers: cotton, wool, silk, linen. Advantages: breathable, comfortable, dyeable. Challenges: shrinkage, higher maintenance.
- Synthetic fibers: polyester, nylon, acrylic. Advantages: durability, wrinkle resistance, color retention. Challenges: lower breathability.
- Blended fabrics: combinations of natural and synthetic fibers for good performance.
Manufacturer Perspective:
- Selection of clothing fabric depends on end-use, comfort, and cost-efficiency.
- We emphasize quality control in weaving/knitting processes to maintain uniformity, strength, and texture.
- Considerations include weight (gsm), thread count, and elasticity.
Applications:
- Everyday apparel: T-shirts, jackets, trousers.
- Activewear: moisture-wicking polyester blends.
- Premium garments: silk, linen, or blended fabrics.
2. Coating Fabric: Enhancing Performance and Durability
Coating fabrics are base textiles treated with a protective layer to improve performance. Common coatings include polyurethane (PU), PVC, and silicone.
Functional Advantages:
- Water Resistance: Coating creates a barrier against moisture, suitable for jackets, rainwear, and outdoor gear.
- Abrasion and Tear Resistance: Protects the fabric in high-stress applications like bags and upholstery.
- Enhanced Appearance: Coatings can add gloss, matte finish, or embossed textures.
Manufacturing Notes:
- Coating can be applied via lamination, calendering, or spraying, depending on desired thickness and performance.
- Quality control focuses on adhesion, uniformity, and durability of the coating.
Applications:
- Rain jackets, outdoor apparel, luggage, furniture upholstery.
- Industrial uses: protective garments, workwear, and tarpaulins.
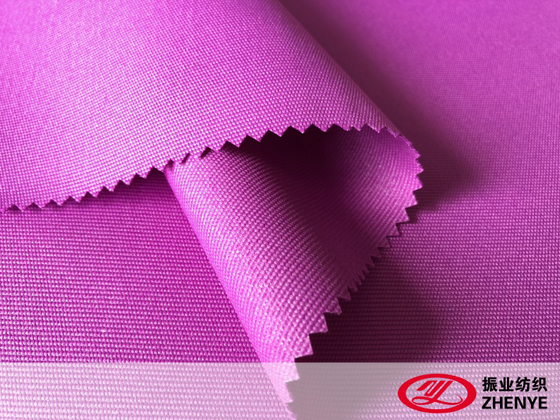
3. Polyurethane Fabric: Composition and Key Properties
Polyurethane fabric (PU fabric) is a type of coating fabric where a layer of polyurethane is bonded to a textile base. It is prized for flexibility, waterproofing, and softness.
Properties:
- Waterproof and Breathable: Advanced PU coatings allow moisture vapor to escape while keeping rain out.
- Lightweight and Flexible: Retains softness of base fabric while adding protective features.
- Durable and Tear-Resistant: Suitable for repeated use in garments, bags, and upholstery.
- Customizable Finish: PU coatings can be smooth, embossed, printed, or laminated with other layers.
Manufacturer Perspective:
- Ensuring proper adhesion of PU to the fabric base is critical.
- Coating thickness and curing process must be carefully controlled to balance flexibility and durability.
- PU fabric production often integrates quality testing for tensile strength, water repellency, and abrasion resistance.
Applications:
- Clothing: rain jackets, windbreakers, softshells.
- Bags and luggage: lightweight, waterproof, and flexible.
- Furniture: PU-coated upholstery for indoor and outdoor use.
4. Comparison Between Clothing, Coating, and PU Fabrics
From a manufacturer's perspective, understanding the differences helps in selecting the right material for specific applications.
| Fabric Type | Base Material | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
| Clothing Fabric | Natural/synthetic fibers | Comfort, breathability, aesthetics | Everyday apparel, activewear, premium garments |
| Coating Fabric | Woven or knitted base | Water resistance, abrasion resistance, durability | Rainwear, workwear, furniture upholstery, bags |
| Polyurethane Fabric | Textile base + PU layer | Flexible, waterproof, lightweight, customizable finish | Jackets, bags, furniture, industrial applications |
Key Insights:
- Clothing fabrics are chosen for tactile comfort and fashion appeal.
- Coating fabrics provide enhanced protection and longevity, especially for outdoor or industrial use.
- PU fabric combines flexibility and water resistance, making it highly versatile for multiple applications.
5. Applications in Apparel, Bags, and Industrial Uses
Clothing Fabric:
- Everyday garments like shirts, trousers, and casual wear prioritize comfort and visual appeal.
- Blended fabrics balance durability, elasticity, and ease of maintenance.
Coating Fabric:
- Rainwear and outerwear: PU or PVC coated fabrics protect from rain and wind.
- Bags and luggage: Coated fabrics increase abrasion resistance, water repellency, and durability.
- Upholstery: Furniture benefits from coated fabrics that resist stains and wear.
Polyurethane Fabric:
- Lightweight jackets, windbreakers, and raincoats use PU-coated fabrics for water resistance without bulk.
- Bags and backpacks use PU layers for flexibility and protection while maintaining design aesthetics.
- Industrial garments and protective covers benefit from PU's durability, tear resistance, and ease of cleaning.
Manufacturer Notes:
- Production processes are carefully tailored to meet customer requirements in terms of finish, color, and functional performance.
- PU and coating fabrics require testing for water repellency, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance before shipping.
6. Quality Control and Manufacturing Practices
From a manufacturer's perspective, quality control is critical for clothing, coating, and PU fabrics:
Key Steps:
- Base Fabric Inspection: Ensure woven or knitted fabrics meet tensile strength, uniformity, and surface quality standards.
- Coating Application Control: Monitor thickness, adhesion, and curing process for PU and other coating fabrics.
Performance Testing:
- Water repellency and breathability tests for PU coatings.
- Abrasion, tear, and tensile tests for durability.
- Colorfastness tests to ensure long-term aesthetics.
Final Inspection: Check for surface defects, coating uniformity, and finished product dimensions.
Practices:
- Use high-quality base fabrics to ensure coating adhesion and long-term performance.
- Maintain precise temperature and humidity control during PU coating application.
- Conduct batch testing for consistency in texture, weight, and performance.
Applications of QC:
- Clothing manufacturers guarantee garments are both comfortable and functional.
- Bag and luggage producers ensure coated fabrics resist wear and water.
- Industrial fabric suppliers provide materials that meet stringent durability standards.
.jpg)
7. Customization and Versatility in Coated and Polyurethane Fabrics
Manufacturers increasingly offer customized solutions using clothing fabric, coating fabric, and polyurethane fabric to meet specific client requirements. By adjusting coating thickness, finish type, or fabric blend, production can target specific functional needs such as water repellency, tear resistance, or surface texture.
Customization Examples:
- Apparel: PU-coated fabrics can be soft and breathable for jackets or windbreakers, while a heavier coating provides rainproof protection for workwear.
- Bags and Luggage: Coating fabric thickness and texture can be adjusted to enhance abrasion resistance, weight, and aesthetics.
- Industrial Uses: Polyurethane-coated fabrics can be reinforced or laminated to meet high-stress applications such as protective covers, tents, or outdoor gear.
From a manufacturer's perspective, this versatility and adaptability allow production to meet a wide range of industry demands without compromising quality or performance. By leveraging the unique properties of PU fabric and coated fabrics, manufacturers deliver products that are functional, durable, and visually appealing, while satisfying both commercial and industrial clients.
From a manufacturer's perspective, clothing fabric, coating fabric, and polyurethane fabric each serve distinct but complementary roles. Clothing fabrics offer comfort and aesthetic appeal, coating fabrics enhance durability and protection, and PU fabrics combine flexibility, water resistance, and strength.
Careful selection of base materials, coating processes, and quality control ensures that the final products meet customer expectations for performance, appearance, and longevity. By understanding the properties and applications of these materials, manufacturers can deliver versatile, high-quality textiles suitable for apparel, bags, furniture, and industrial uses.


 EN
EN
 English
English Español
Español 中文
中文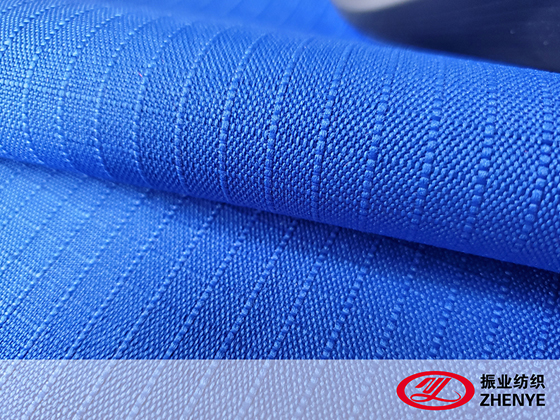
.jpg)
-1.jpg)
-1.jpg)