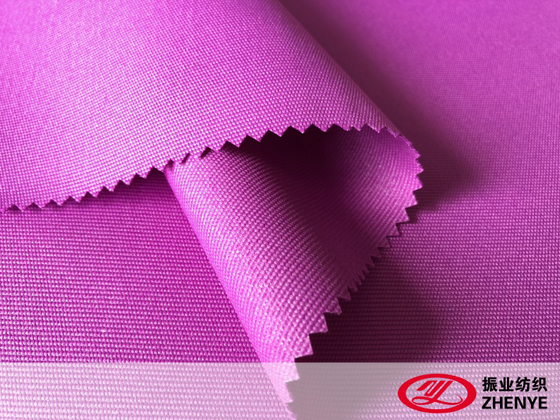
Eco-friendly fabrics, recycled polyester, and sustainable textiles are becoming essential in modern textile manufacturing due to increasing environmental awareness. Manufacturers are increasingly focused on producing textiles that reduce resource consumption, minimize pollution, and maintain high quality and performance standards.
Recycled polyester (RPET) and other sustainable fabrics provide a solution by transforming post-consumer or post-industrial waste into usable fibers, offering durability, versatility, and environmental benefits. Understanding the materials' properties, processing techniques, and practical applications allows manufacturers to create high-performance textiles that meet both functional and eco-conscious requirements.

1. Types of Eco-Friendly Fabrics
Key Points:
- Recycled Fibers: Polyester, nylon, cotton blends sourced from post-consumer waste like PET bottles and old garments.
- Organic Natural Fibers: Organic cotton, hemp, bamboo – grown with reduced pesticides and water consumption.
- Blended Fabrics: Combining recycled polyester with organic cotton or other fibers to improve texture, strength, and sustainability.
Manufacturer Perspective:
- Selection depends on end-use: apparel, bags, furniture, or industrial textiles.
- Focus on quality control to ensure fiber consistency, strength, and colorfastness.
- Processing must balance eco-conscious methods with production efficiency.
Applications:
- Apparel: T-shirts, jackets, activewear.
- Bags: Backpacks, tote bags.
- Home textiles: Curtains, bed linens, upholstery.
2. Recycled Polyester (RPET) Properties and Production
Recycled polyester fabric (RPET) is made from post-consumer PET bottles or post-industrial polyester waste.
Key Properties:
- Durability: Strong and resistant to wear and tear.
- Water Resistance and Easy Maintenance: Suitable for everyday clothing and bags.
- Color Retention: Holds dye well without fading.
- Softness and Versatility: Comparable to virgin polyester.
Manufacturing Considerations:
- Sorting and cleaning PET bottles or waste is essential to remove impurities.
- Fibers are melted and spun into yarns with consistent thickness and strength.
- Quality control ensures tensile strength, fabric uniformity, and performance standards.
Applications:
- Apparel: T-shirts, jackets, activewear.
- Bags and luggage: Backpacks, duffels, tote bags.
- Home textiles: Cushions, bedding, curtains.
3. Sustainable Textile Practices in Manufacturing
Sustainable textile production involves processes that minimize environmental impact.
Key Points:
- Water and Energy Efficiency: Reduce water usage in dyeing and washing, and optimize energy in spinning and weaving.
- Chemical Management: Use non-toxic dyes and finishing agents.
- Waste Reduction: Reuse or recycle offcuts and production scraps.
Manufacturer Perspective:
- Sustainable practices reduce production costs in the long term by minimizing waste and improving efficiency.
- Adhering to eco-friendly certifications such as Global Recycled Standard (GRS) or OEKO-TEX ensures traceability and market credibility.
- Testing for durability, colorfastness, and strength ensures products meet performance standards while remaining sustainable.
Applications:
- Mass-market apparel and eco-conscious brands.
- Industrial textiles for upholstery, bags, and protective gear.
4. Functional Advantages of Recycled Polyester and Eco-Friendly Fabrics
Key Benefits:
- Environmental Impact: Reduces landfill waste and lowers carbon footprint.
- Cost Efficiency: Repurposing waste materials can reduce raw material costs.
- Durability and Performance: Comparable or better than virgin polyester for tensile strength and wear resistance.
- Versatility: Suitable for garments, bags, home textiles, and industrial applications.
Manufacturer Perspective:
- RPET production allows scaling of eco-friendly fabrics while maintaining quality.
- Ability to customize weight, texture, and finishing for different product lines.
- Emphasis on quality testing ensures durability and resistance to abrasion, water, or UV exposure.
Applications:
- Lightweight jackets, activewear, tote bags, backpacks.
- Upholstery for furniture and automotive interiors.
- Industrial protective textiles.
5. Dyeing and Finishing Processes for Sustainable Fabrics
Key Points:
- Digital Printing: Eco-friendly method with reduced water and chemical usage.
- Water-Based Dyes: Non-toxic, energy-efficient, and safer for workers.
- Finishing Treatments: Anti-microbial, water-repellent, and wrinkle-resistant finishes can be applied without compromising sustainability.
Manufacturer Perspective:
- Process optimization ensures consistent dye penetration and even color distribution.
- Testing for shrinkage, tensile strength, and abrasion ensures fabric performance.
- Emphasis on minimal chemical use to maintain eco-friendly certification compliance.
Applications:
- Fashion apparel with vibrant patterns.
- Bags and luggage requiring coated or printed surfaces.
- Home textiles with decorative and functional finishes.
6. Applications Across Different Industries
- Fashion Industry:
Activewear, casual wear, jackets, and premium garments.
RPET and blended eco-friendly fabrics balance comfort, durability, and style.
- Bags and Accessories:
Backpacks, tote bags, and laptop sleeves benefit from RPET for strength and water resistance.
- Home Textiles:
Cushions, bedding, curtains, and upholstery using recycled fabrics provide eco-friendly options for interiors.
- Industrial Applications:
Protective workwear, tarpaulins, and equipment covers use coated eco-friendly fabrics for durability and water resistance.
- Manufacturer Perspective:
Material selection is critical to meet specific end-use requirements.
Performance testing for tear resistance, abrasion, and color retention is mandatory before shipment.

7. Quality Control and Manufacturing Standards
Key Steps in Manufacturing:
- Material Inspection: Ensure recycled polyester and eco-friendly fibers meet quality standards.
- Production Monitoring: Check spinning, weaving, and knitting consistency.
- Coating and Finishing Control: Verify adhesion, smoothness, and functional properties like water repellency.
- Performance Testing: Test tensile strength, abrasion resistance, colorfastness, and dimensional stability.
- Certification Compliance: Ensure adherence to standards like OEKO-TEX and GRS.
Manufacturer Perspective:
- Emphasis on repeatable quality ensures reliability across product lines.
- Balancing sustainability and performance requires precision at each production stage.
- Continuous testing allows manufacturers to confidently supply apparel, bags, home textiles, and industrial products that meet customer and regulatory expectations.
Applications:
- Eco-conscious apparel brands rely on verified recycled polyester fabrics.
- Bags and luggage producers require consistent strength and durability.
- Industrial textile suppliers prioritize functional reliability in protective fabrics.
8. Customization and Functional Applications of Eco-Friendly Fabrics
Manufacturers can tailor eco-friendly fabrics, recycled polyester, and sustainable textiles to meet specific performance and aesthetic requirements, making them highly versatile for various industries. By adjusting fiber blends, coating thickness, finishing treatments, or fabric textures, manufacturers can create textiles with specialized properties without compromising environmental standards.
Apparel: Recycled polyester can be blended with organic cotton for jackets, sportswear, or casual wear, balancing comfort, stretchability, and durability. Specialized coatings or laminates can make garments water-resistant or windproof while maintaining softness.
Bags and Accessories: Fabric thickness, density, and finishing can be adjusted to enhance tear resistance, water repellency, and structural support for backpacks, tote bags, and luggage.
Home and Industrial Textiles: Sustainable textiles can be treated with anti-microbial, flame-retardant, or stain-resistant finishes for furniture upholstery, curtains, protective covers, and industrial applications.
Manufacturer Perspective:
- Functional customization allows manufacturers to satisfy diverse client needs, from fashion brands to industrial suppliers.
- Rigorous testing ensures that tailored eco-friendly fabrics retain strength, durability, and colorfastness while meeting specific functional demands.
- This adaptability positions recycled polyester and sustainable textiles as reliable materials for products requiring both environmental responsibility and high performance.
9. Summary of Key Material Advantages
Eco-friendly fabrics, recycled polyester, and sustainable textiles offer a combination of durability, versatility, and environmental responsibility. From a manufacturer's perspective, these materials allow for high-performance products while reducing waste and conserving resources. RPET and blended sustainable textiles maintain tensile strength, color retention, and abrasion resistance, making them suitable across apparel, bags, home interiors, and industrial applications. Optimized dyeing, finishing, and coating processes ensure functionality without compromising sustainability.
By implementing strict quality control and production standards, manufacturers can produce reliable, market-ready textiles that meet the growing consumer demand for eco-conscious fabrics without sacrificing performance or aesthetic appeal.


 EN
EN
 English
English Español
Español 中文
中文
-1.jpg)
-1.jpg)
-1.jpg)
-1.jpg)