In recent years, the textile industry has faced growing scrutiny due to its environmental footprint. Traditional polyester material and other synthetic fabrics, while durable and versatile, are derived from petrochemicals and contribute to plastic waste and greenhouse gas emissions. In response, recycled fabric has emerged as a sustainable alternative that helps mitigate environmental damage while maintaining high performance.
These sustainable fabrics are increasingly popular across fashion, home textiles, bags, and industrial applications, combining functionality with eco-conscious innovation.
1. Understanding Recycled Fabric
Recycled fabric is made from post-consumer waste or post-industrial scraps, such as discarded PET bottles, textile offcuts, or outdated garments. By converting waste materials into high-quality fibers, recycled fabric reduces landfill waste, conserves energy, and lowers carbon emissions. One of prominent examples is recycled polyester fabric (RPET), which transforms plastic bottles into versatile, durable, and environmentally responsible textiles. Across industries, recycled fabric has become a core component in sustainable fabrics production, offering an alternative that is both practical and eco-friendly.
2. Polyester Material and Its Environmental Impact
Polyester material is a widely used synthetic fiber known for its durability, wrinkle resistance, and cost-effectiveness. It is commonly applied in clothing, bags, upholstery, and industrial textiles due to its ability to hold shape, resist water, and maintain color over time.
However, traditional polyester has notable environmental drawbacks. Being petroleum-based, its production consumes non-renewable resources and generates significant carbon emissions. Additionally, polyester is non-biodegradable, contributing to long-term waste problems, especially in oceans and landfills. The rise of recycled polyester fabric (RPET) has addressed many of these concerns. By repurposing existing plastic waste, RPET reduces the environmental impact of polyester while retaining its desirable properties.
From a manufacturer's perspective, using recycled fabric and RPET in products such as backpacks, sportswear, and home textiles allows companies to maintain quality standards while supporting sustainability initiatives. It provides a way to combine durability, water resistance, and lightweight design with a reduced ecological footprint.
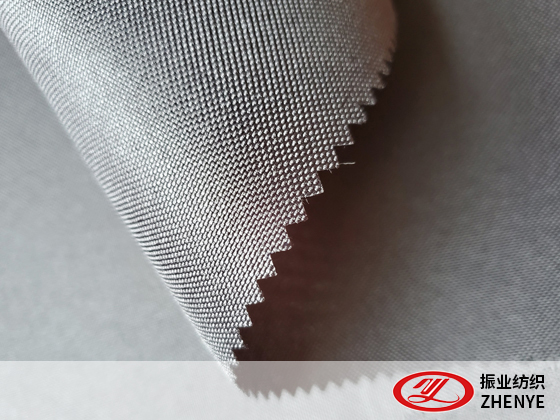
3. Benefits of Using Recycled Polyester and Sustainable Fabrics
Sustainable fabrics such as RPET and other recycled fibers offer multiple advantages beyond environmental protection.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint:
Recycled polyester reduces energy consumption compared to virgin polyester.
For every kilogram of RPET produced, significant amounts of CO2 emissions are avoided, making it a greener option for manufacturers.
- Plastic Waste Reduction:
RPET transforms discarded PET bottles and other plastic materials into reusable fibers.
Each product made from recycled fabric helps divert waste from landfills and oceans.
- Durability and Performance:
RPET and other recycled fabrics maintain the strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity of conventional polyester.
They can be treated with coatings such as PU or PVC for enhanced water resistance, making them suitable for bags, backpacks, and outerwear.
- Versatility Across Industries:
Sustainable fabrics can be used in fashion, outdoor gear, home textiles, and industrial applications.
They support both aesthetic and functional requirements, such as vibrant color retention, smooth texture, and structural integrity.
- Brand Value and Consumer Appeal:
Eco-conscious consumers increasingly prefer products made from recycled fabric.
Companies that adopt sustainable textiles demonstrate corporate responsibility, enhancing brand reputation and market competitiveness.
4. Applications of Recycled Fabric in Modern Fashion and Industry
The versatility of recycled fabric has made it an integral component in modern manufacturing.
- Fashion Industry:
Recycled polyester fabric is used in casual apparel, sportswear, jackets, and scarves.
Its ability to hold vibrant colors, combined with the softness of textile blends, makes it ideal for both functional and aesthetic purposes.
- Bags and Luggage:
Products such as backpacks, duffels, and tote bags frequently utilize Rpet 600D PU Coating Fabric for added water resistance and durability.
Recycled fabrics maintain structural integrity while offering eco-friendly branding opportunities.
- Home Textiles:
Curtains, upholstery, and bedding made from sustainable fabrics deliver performance and environmental benefits.
Recycled fibers can mimic the texture and comfort of natural fibers while reducing water and energy usage.
- Industrial Applications:
Recycled polyester is used in tents, protective gear, and outdoor equipment due to its lightweight and tear-resistant qualities.
- Emerging Trends:
Digital printing on recycled fabrics is gaining traction, allowing customization while maintaining sustainability.
Blends of recycled polyester with cotton, linen, or other natural fibers provide hybrid textiles suitable for eco-conscious fashion and lifestyle products.
5. Challenges and Considerations for Recycled and Sustainable Fabrics
Despite the benefits, manufacturers face several challenges when using recycled fabric and RPET.
- Consistency in Fiber Quality:
Recycled materials may vary in thickness, strength, or color, requiring careful blending and quality control.
- Color Matching and Finishing:
Achieving consistent color and surface finish can be more challenging with recycled fibers compared to virgin polyester.
- Cost Considerations:
While RPET reduces environmental impact, production costs may be slightly higher due to sorting, cleaning, and processing of recycled materials.
- Consumer Education:
Brands need to inform consumers about the value of sustainable fabrics, highlighting durability, eco-friendliness, and ethical production.
- Recycling Limitations:
Some blends, especially fabrics mixed with non-recyclable fibers, may be harder to recycle fully.
Manufacturers must innovate with chemical recycling and circular economy strategies to improve sustainability.
Solutions: Certifications such as the Global Recycled Standard (GRS) help ensure traceability, quality, and sustainability of recycled fabrics.

6. Future Trends in Sustainable Fabrics
The future of polyester material and recycled fabric is closely tied to technological innovation and consumer demand for eco-conscious products.
- Bio-Based Polyester Alternatives:
Researchers are developing polyester from renewable sources such as corn or sugarcane, complementing recycled polyester.
- Integration into High-Performance Applications:
Recycled polyester fabric is increasingly used in sportswear, outdoor gear, and technical textiles, combining sustainability with functionality.
- Circular Economy and Upcycling:
Take-back programs and fabric upcycling help create closed-loop systems where textiles are continuously reused.
- Advanced Digital Printing:
Printing technology optimized for recycled fabrics allows complex designs, vibrant colors, and functional coatings while maintaining sustainability.
- Consumer-Driven Market Shift:
Sustainable fabrics are moving from niche products to mainstream offerings, driven by environmental awareness and regulatory policies.
- Hybrid Fabric Blends:
Combining recycled polyester with organic cotton, linen, or other natural fibers provides textiles that are environmentally responsible yet comfortable and stylish.
The textile industry is evolving toward sustainability, and recycled fabric plays a pivotal role in reducing environmental impact. Polyester material, once criticized for its ecological footprint, has been transformed through recycled polyester fabric (RPET) and innovations like Rpet 600D PU Coating Fabric. These sustainable fabrics provide the durability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal expected by consumers, while simultaneously addressing concerns about plastic waste, energy consumption, and carbon emissions.
From fashion to home textiles, bags, and industrial applications, manufacturers and brands now have the tools to deliver high-performance products without compromising the environment. By embracing recycled fabric, the textile industry can move closer to a circular economy and a more sustainable future, balancing innovation, functionality, and environmental responsibility.


 EN
EN
 English
English Español
Español 中文
中文
-1.jpg)
.jpg)
-1.jpg)
-1.jpg)
-1.jpg)