Origin and Early Uses: From Industrial Textiles to Everyday Items

300D fabric appeared as a practical solution for industrial and outdoor applications in the late 20th century.
Industrial Introduction: Early 300D fabrics were primarily made from nylon or polyester fibers. Their moderate thickness offered a balance between strength and light weight, making them suitable for items such as tool pouches, safety gear, and tarpaulins.
Outdoor Applications: The durability and resistance to wear led to its use in outdoor equipment such as tents, backpacks, and protective covers.
Function: The initial adoption focused on products that required reliable performance under moderate mechanical stress while remaining manageable in weight and flexibility.
Significance: Understanding its early uses highlights why 300D fabric was chosen over thinner fabrics for functional reliability and over heavier fabrics for ease of handling.
Material Innovations: Nylon, Polyester, and Hybrid Fibers
Over time, the development of 300D fabric involved the introduction of different fiber types and hybrid materials.
- Nylon Fibers: Early versions often used nylon for its strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity. Nylon fabrics resisted tearing while remaining flexible enough for complex designs.
- Polyester Fibers: Polyester-based 300D fabrics gained popularity for improved UV resistance, color retention, and resistance to moisture absorption. These characteristics expanded its use in outdoor and consumer products.
- Hybrid Blends: Modern 300D fabrics sometimes combine nylon and polyester or incorporate other fibers, improving performance attributes such as water repellence, abrasion resistance, and weight distribution.
- Function: Material innovation allowed 300D fabrics to meet a wider range of requirements, including outdoor durability, light weight, and improved texture, supporting broader applications.
Weaving and Finishing Techniques: Enhancing Functionality
Advances in weaving and finishing techniques have contributed to the versatility and performance of 300D fabric.
Weaving Methods: 300D fabrics are typically woven in plain or ripstop patterns. Ripstop weaving integrates reinforced threads at intervals to prevent tearing, enhancing durability without significantly increasing weight.
Coatings and Laminates: Coatings such as polyurethane, PVC, or silicone enhance water resistance, abrasion resistance, and durability. Laminated finishes allow the fabric to serve as protective layers in luggage, tents, or rainwear.
Surface Treatments: Treatments such as anti-microbial, flame-retardant, or UV-resistant coatings extend the fabric's utility in specific environments, making it suitable for technical and consumer products.
Function: Weaving and finishing techniques ensure that 300D fabric performs well under different conditions while maintaining its lightweight nature and adaptability for various product designs.
Modern Applications: From Outdoor Gear to Everyday Products
The development of 300D fabric has led to a wide range of applications in contemporary products.
Bags and Backpacks: Its balance of weight and strength makes it ideal for daily-use backpacks, travel bags, and laptop cases.
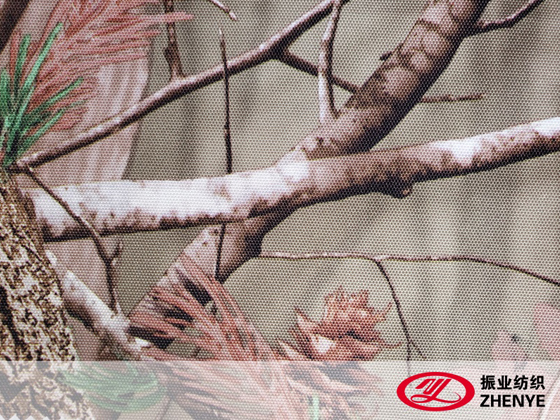
Outdoor Equipment: Tents, protective covers, and camping gear rely on 300D fabric for its tear resistance and durability.
Protective Gear and Apparel: Some garments, such as jackets, aprons, or uniforms, incorporate 300D fabric for moderate protection against wear and environmental exposure.
Home and Commercial Products: Furniture upholstery, storage organizers, and decorative items sometimes use 300D fabric, benefiting from its texture, color retention, and manageability.
Function: The expansion of applications demonstrates the adaptability of 300D fabric and its relevance in both technical and consumer-oriented products.


 EN
EN
 English
English Español
Español 中文
中文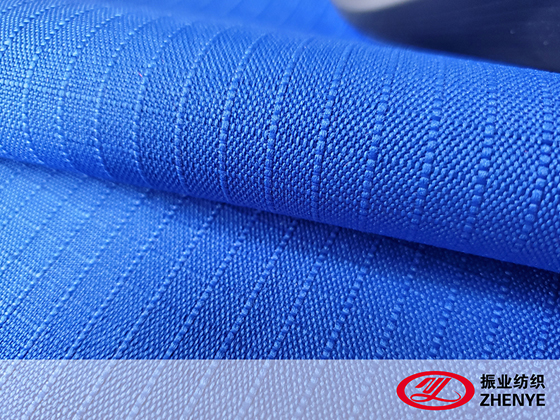

.jpg)
.jpg)
-1.jpg)
-1.jpg)